In all market cycles, commercial real estate firms are better positioned to achieve successful results with leaders who are strong, confident, and authentic, qualities demonstrated by the dozens of speakers at the 2025 Real Estate Pride Roundtable in New York City.
Q2 2020 Small Multifamily Investment Trends Report
Small Multifamily Weathers the Storm

- Small multifamily prices fell 5.6% from a year ago.
- Cap rates held steady as risk-free rates fell.
- Small multifamily LTVs dropped by 360 bps from the prior quarter.
State of the Multifamily Market
When the Nobel Committee meets this year to decide who has made the most meaningful contributions to the field of economics, they might as well give the honor to the epidemiologists. Right now, those experts are providing key indicators of the future of markets throughout the world shaped by the course of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Disorganized and inconsistent reopenings in the U.S. economy have fanned the domestic spread of the coronavirus. There is a non-zero probability that parts of the country will need future lockdowns to curb the outbreak’s acceleration. Even without a formal lockdown, the present risk of the virus continues to limit the speed in which the U.S. economy can recover.
While the number of people filing for initial unemployment dropped for 15 consecutive weeks following the late-March surge, the measure is once again starting to rise. Worse yet, the recent “low” of 1.3 million weekly jobless claims is more than double any weekly observation of the Great Financial Crisis. Nonetheless, the total number of people receiving unemployment benefits is falling in aggregate, suggesting that, for now, the pace of rehiring is outpacing the rate of new job losses.
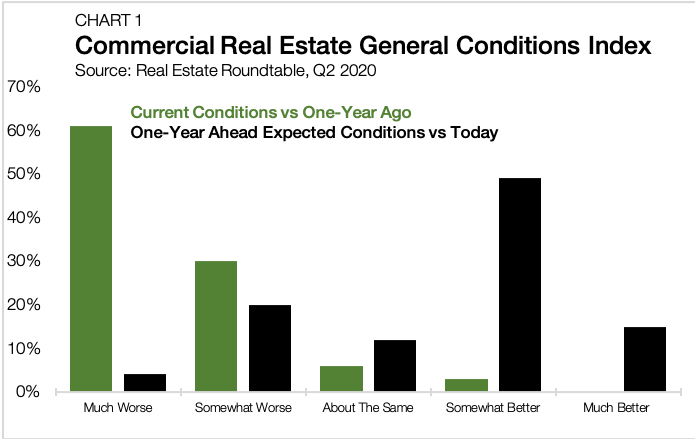
According to the Bureau of Economic Analysis, the U.S. economy contracted at an unsightly 32.9% annual rate in the second quarter, the worst reading ever. Yet a majority (63.8%) of economists polled by the WSJ Economic Forecasting Survey believe that the U.S. will begin its recovery in the third quarter. The outlook for commercial real estate tracks closely with the rest of the economy. Unsurprisingly, 91% of respondents in the Real Estate Roundtable’s 2020 Q2 Sentiment Index report worse business conditions today than one year ago (Chart 1). Looking ahead, 64% of respondents believe that commercial real estate conditions will improve over the next 12 months.
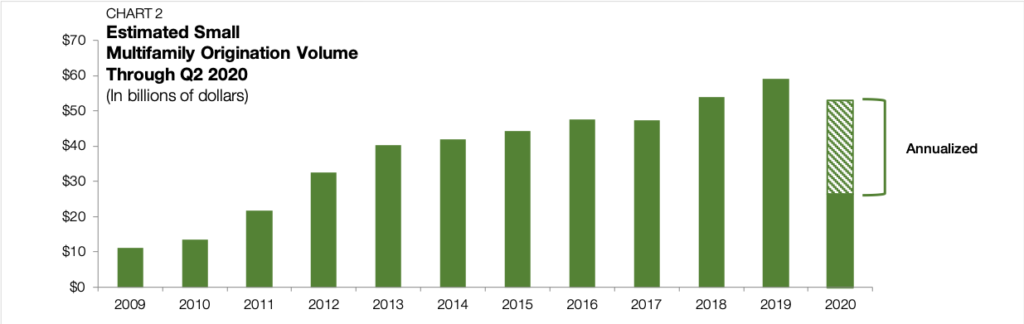
Within the small multifamily sector, COVID-19 is actively transforming household preferences, perceptions of risk and access to liquidity. Refinancing requests make up an outsized share of new lending activity as forward-looking uncertainty dampens demand for new investment sales.
According to Chandan Economics, distressed sales are weighing down on market-clearing asset prices, with small multifamily valuations falling 5.6% from a year ago. However, cap rates are continuing to hold steady as declining risk-free rates and rising risk premiums balance against one another. Overall, while small multifamily is working through its fair share of coronavirus-related pain, the presence of the agencies and the relative stability of underlying user demand are resulting in the sector’s outperformance of other property types, other than industrial.
Lending Volume of Multifamily Loans
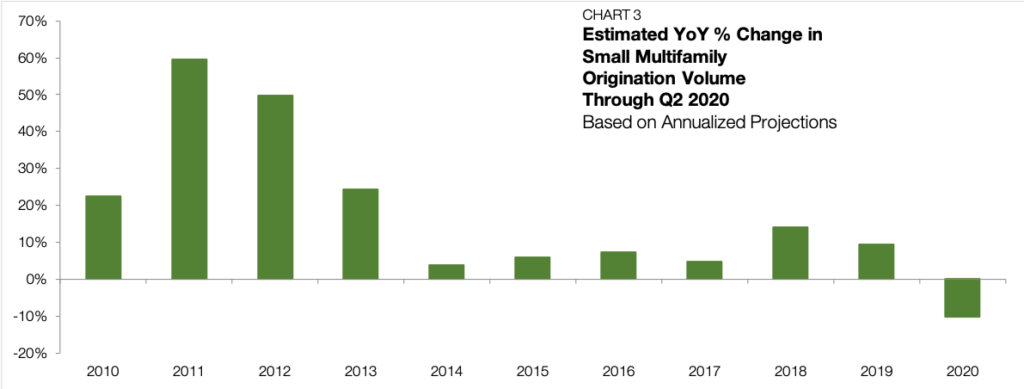
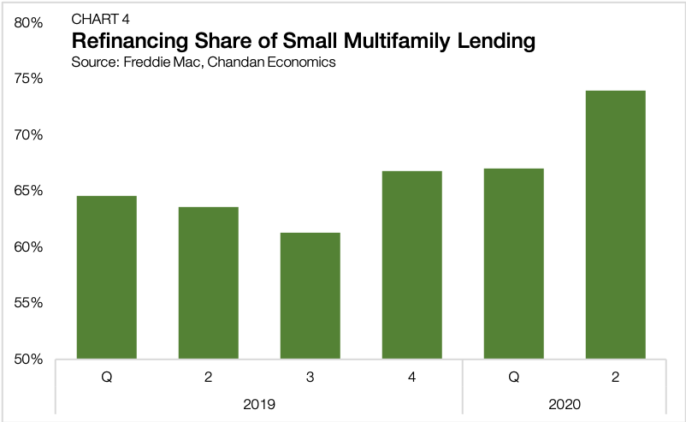
Meanwhile, demand for refinancing continues to soar. According to Chandan Economics’ analysis of Freddie Mac’s Small Balance Loan securitizations, refinancing accounted for 74% of small multifamily lending in the second quarter, up from 61% in Q3 2019 (Chart 4). Falling interest rates have provided existing owners the opportunity to access accrued equity while lowering monthly debt servicing costs.
The uptick in refinancing activity helped to moderate the total small multifamily lending figure. Nevertheless, on balance, the second quarter’s annualized 10.3% decline in total lending speaks to the uncertainty, challenges, and reluctance in the current market environment. A lack of confidence in the economic outlook has both borrowers and sellers reducing their speed until the path ahead clears.
Small multifamily prices, as measured by the Arbor Small Multifamily Price Index, fell in the second quarter of 2020 by 5.6% — the first year-over-year decline since 2010 (Chart 5 and Chart 6).(The Arbor Small Multifamily Price Index (ASMPI) uses model estimates of small multifamily rents and compares them against small multifamily cap rates. The index measures the estimated average price appreciation on small multifamily properties with 5 to 50 units and primary mortgages of $1 million to $7.5 million. For the full methodology, visit arbor.com/asmpi-faq.)
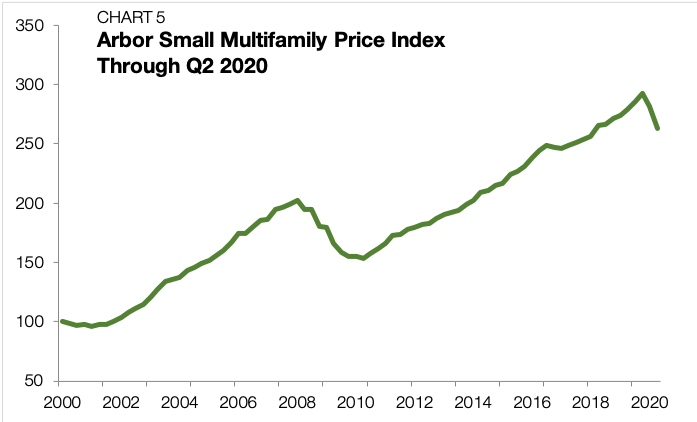
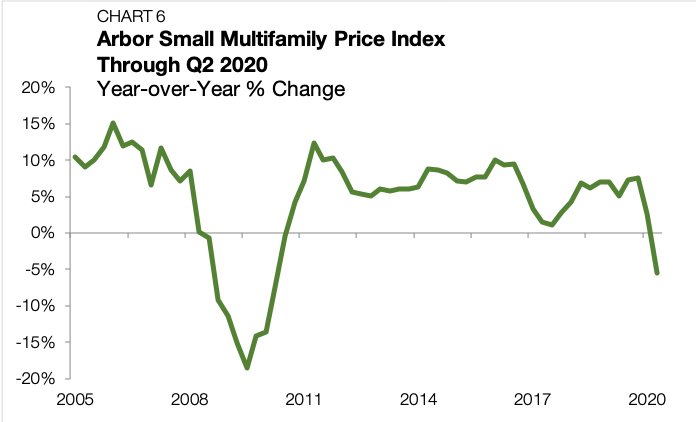
The reading marks an inflection point for a market that had unabated annualized price growth for 38 consecutive quarters. The price distortion is a symptom of the hyper-uncertainty affecting both potential buyers and existing owners. Buyers are applying more conservative property-income forecasts in their acquisition models, haircutting executable valuations. Owners, on the other hand, are trying to weather the storm.
Listing a property in a recessionary market, let alone during a pandemic, requires a seller to accept a discount compared to what they might have expected to achieve a year ago or a year from now. Would-be sellers who have the cashflows and access to financing are choosing to postpone dispositions. Of course, not all owners have that luxury. The ticker tape of transactions in today’s market reflects an outsized share of distressed sales.
Small Multifamily Cap Rates & Spreads
National average cap rates for small multifamily properties narrowed by 5 bps in the second quarter of 2020, reaching 5.8% (Chart 7 and Chart 8). In the first quarter, cap rates widened by 21 bps, and there was some concern that they would further inch up as the economic downturn continued. Instead, small multifamily cap rates held steady due to a pricing tug-of-war. Declining risk-free interest rates have the effect of reducing cap rates, while increased operational risks have the effect of widening cap rates. When both phenomena happen at the same time, the net effect is cap rate stability.
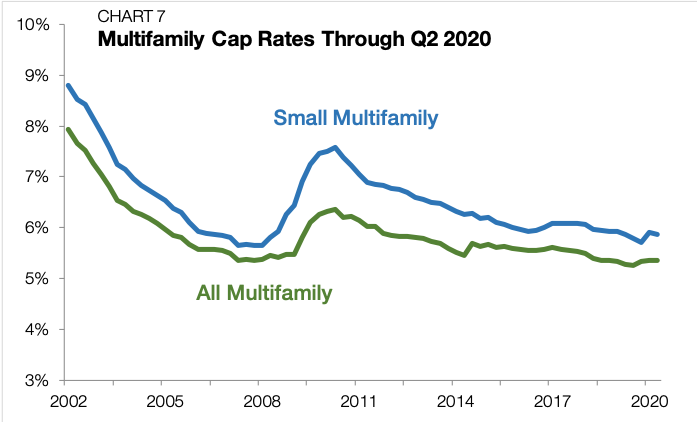
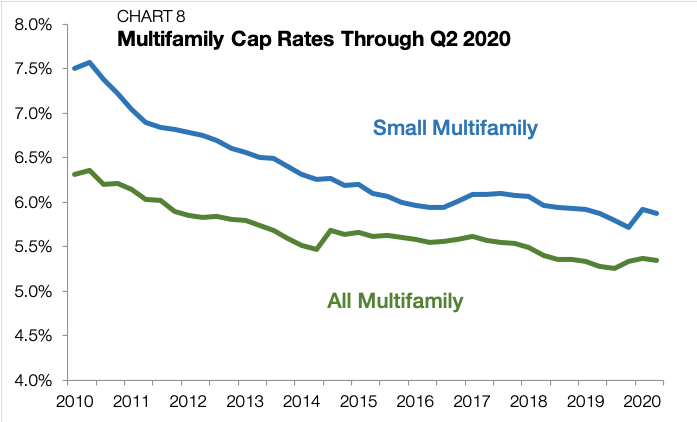
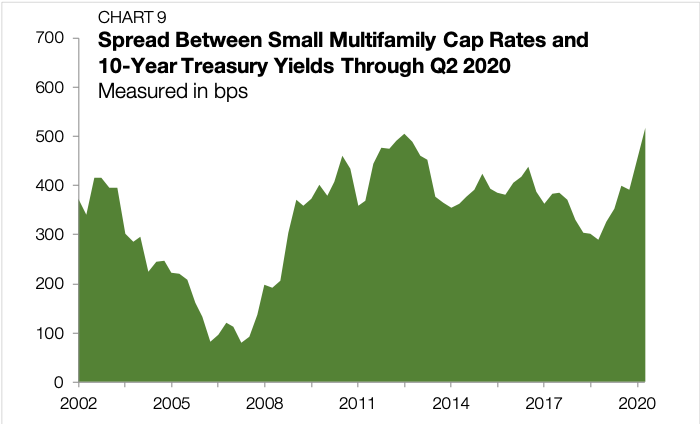
Through the last three months, 10-year Treasury yields averaged just 0.69% — the lowest quarterly reading on record. As the state of the world has become less certain and market risks are more difficult to gauge, investors prefer “safe-haven” assets, causing the price of Treasurys to rise and their yields to fall.
The risk-free interest rate is embedded within the yield structure of all other market returns, including cap rates. Investors require additional compensation when accepting additional risk. We can infer this risk premium in small multifamily by looking at the difference between cap rates and Treasurys. Through the second quarter, the spread stood at 518 bps, the highest level on record (Chart 9).
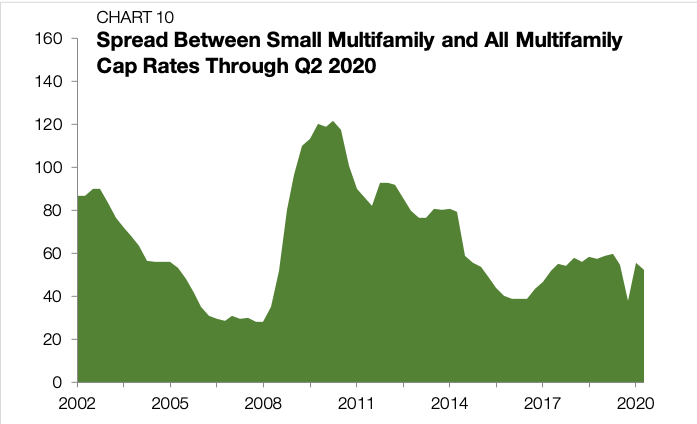
The cap rate spread between small multifamily and the rest of the sector stood at 52 bps through the second quarter of 2020, barely budging from the first quarter (Chart 10). The CARES Act stimulus, additional unemployment benefits, and eviction moratoriums have all had an effect of providing housing stability in a period of crisis. With many of these protective measures set to expire, the resiliency of property-level cash flows is a resurgent topic of debate.
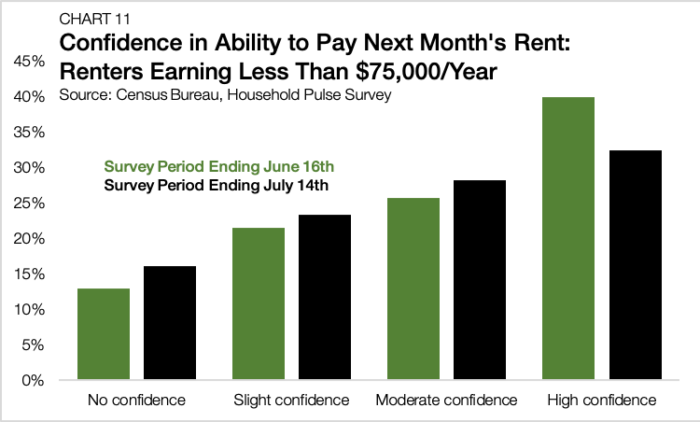
According to a Chandan Economics analysis of the Census Bureau’s mid-July Weekly Pulse Survey, 39.4% of renters earning less than $75,000 either had no confidence or slight confidence in their ability to pay the next month’s bill — jumping 4.9% from mid-June (Chart 11). Higher earning renters did not express the same level of concerns. For tenants earning $75,000 to $150,000 and above $150,000, only 18.5% and 6.6% of renters, respectively, are pessimistic about their ability to pay August rent. Small multifamily renters tend to earn less than their large multifamily neighbors, making small assets an area to watch in rent collections.
Simultaneously, small multifamily trends suggest renters are comparatively less transient and less likely to transition into homeownership in the medium term. With COVID-19 causing many young households to reconsider their housing location preferences, the small multifamily subsector may prove more resilient in re-leasing and maintaining stable occupancies over the medium term. There are many moving pieces in play, and how small multifamily attenuates the forward-looking risks compared to the rest of the sector is a far from settled discussion.
Leverage and Debt Yields in Multifamily Market
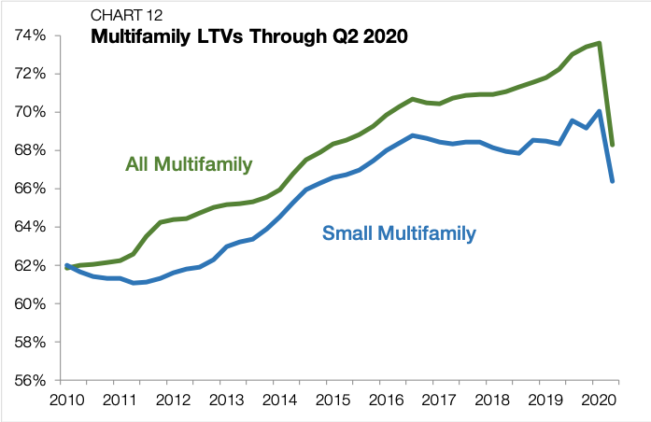
Loan-to-value ratios (LTVs) averaged 66.4% on small multifamily loans originated during the second quarter of 2020, a near vertical drop of 360 bps from the first quarter (Chart 12). The trends in the broader multifamily market were similar, where LTVs nosedived to 68.3%, backtracking to 2016 levels. According to Chandan Economics’ initial estimates, the LTV spread between small multifamily and all multifamily currently stands at 313 bps, the highest reading in six quarters. The marketwide pullback in LTVs suggests that lenders are appropriately taking caution. In a period where price discovery remains elusive, building in larger equity cushions is an effective way to protect originators against market volatility and borrower defaults.
Multifamily Market Outlook
Like every other sector, small multifamily is facing a mix of shared and unique challenges as a result of the COVID-19 economic downturn. Uncertainty in the macroeconomic outlook will continue to keep many would-be buyers on the sidelines. The income profile of small multifamily renters, coupled with the ongoing disruption of labor markets, makes the sector more vulnerable to deteriorating rent collections, especially as the breadth of supportive government relief efforts begin to wane. However, the small asset subsector may prove to be one of the more resilient areas of multifamily over the medium term as these properties are more likely to contain renters-by-necessity rather than renters-by-choice. All else equal, while small multifamily sector will not go unscathed, the depth of agency support and stickiness of underlying user demand will insulate it from the worst of COVID-19’s economic toll.
For more small multifamily research and insights, visit arbor.com/articles